
Emerging AI Tools for Open Access Repositories
AI is reshaping how open access repositories operate. These platforms, essential for storing and sharing scholarly works, are now leveraging AI to automate tasks like metadata tagging, improve search capabilities, and streamline document processing. This article highlights five AI tools transforming repository workflows:
- Sourcely: Simplifies literature searches with reverse search capabilities and automated citation management.
- H2O.ai: Uses advanced OCR and machine learning to process unstructured PDFs into searchable data.
- MindsDB: Connects to multiple data sources, enabling real-time data queries and synchronization.
- OpenCV: Focused on visual data, it automates tasks like table detection and image analysis in documents.
- Keras: Provides deep learning tools for natural language processing and computer vision, integrating easily with existing systems.
Each tool offers unique strengths, from enhancing search efficiency to automating complex data extraction, helping repositories keep up with growing research demands. Below, we dive into their features, use cases, and compatibility with repository systems.
DSpace Reimagined: The Next Generation of AI-Powered Repositories
1. Sourcely
Sourcely is changing the way researchers navigate open access repositories by combining AI with advanced indexing. This tool has indexed over 200 million peer-reviewed research papers, making it a go-to resource for academics. Unlike traditional search engines that rely on keywords, Sourcely uses a reverse search method. Researchers can paste entire paragraphs or essays to find credible sources that match their content. With over 100,000 users, it’s become a key tool for streamlining research.
PDF Handling
One standout feature of Sourcely is its ability to provide direct links to free PDFs for many academic sources, so users can access full-text documents without switching platforms. It also offers helpful metadata, including citation counts, publication dates, and journal reputations, to validate source credibility. For instance, in March 2025, a 1,000-word bioacoustics paper was matched with relevant sources in just 10 seconds, and citable excerpts were identified in 20 seconds. This efficiency makes Sourcely a powerful assistant for research tasks.
Automation Features
Sourcely simplifies tedious research processes through automation. It matches uploaded text to relevant sources, saving users from manual keyword searches. Before downloading a full PDF, researchers can review concise, AI-generated 200-word summaries to quickly gauge the material's relevance. The platform also highlights citable sections within documents and supports exporting references in popular formats like MLA, APA, BibTeX, Harvard, and IEEE.
"One of the limitations of databases like Google Scholar is that they let you search using only keywords. But what if you want to search using whole paragraphs or your notes? Sourcely is an AI-powered app that will let you do that".
- Mushtaq Bilal, PhD, Postdoctoral Researcher
Scalability
Sourcely’s infrastructure supports its extensive database and diverse features, making it a scalable solution for researchers. Pricing plans cater to different needs, from a one-time $7.00 fee for 2,000 characters to subscriptions at $17.00 per month or $167.00 annually. For those seeking long-term access, the lifetime Believer Plan costs $347.00. Additionally, the updated Library feature allows users to organize saved sources into folders, making it easier to manage resources for multiple projects. This combination of flexibility and organization ensures researchers can efficiently handle their academic workload.
2. H2O.ai

H2O.ai has revolutionized the way open access repositories handle documents with its Document AI platform. By leveraging advanced technologies like ICR, OCR, and NLP, the platform transforms unstructured PDFs into structured, searchable data. A standout example of its application came in 2022 when UCSF Health adopted H2O Document AI to automate medical referral processing. The shift from manual data extraction to an automated workflow marked a significant improvement. Bob Rogers, Expert in Residence for AI at UCSF, highlighted the collaboration's potential:
"Now that the UCSF-H2O.ai collaboration team has delivered, it opens up many possibilities".
This transformative technology deserves a closer look at its automation features.
Automation Features
H2O.ai's platform simplifies repository management with its Universal Scoring Pipelines (USP), a system that seamlessly connects various processes - from PDF intake to image normalization and custom post-processing. It even automates data labeling, generating new labels and correcting errors as needed. To ensure maximum accuracy, the platform employs the E3 Best OCR method, which first tries direct text extraction from PDFs. If that fails, it switches to DocTR EfficientNet B3 OCR. Impressively, the system supports over 40 languages and recommends a resolution of 300 DPI for best results .
Scalability
The platform's scalability is another major strength, making it capable of handling enormous volumes of documents. Thanks to distributed in-memory processing, it achieves speeds up to 100× faster. It integrates seamlessly with existing infrastructures like Hadoop/YARN, Spark, and Kubernetes clusters, and it supports NVIDIA GPU acceleration for even greater efficiency. With over 18,000 organizations worldwide relying on H2O.ai, its impact is widespread. In February 2026, Change Healthcare processed billions of claims using H2O.ai. Adam Sullivan, Director at Change Healthcare, described its effectiveness:
"H2O has been the driver for building models at scale. We are talking about billions of claims".
To further conserve resources, the system employs "sleeping pipelines", which automatically scale down to zero replicas when idle, only ramping up when new documents are added.
Repository Compatibility
H2O.ai ensures compatibility across various repository systems through its REST API, which processes documents and outputs results in a flat JSON format. It integrates with major cloud storage providers such as S3, Azure Blob Storage, and MinIO . A striking demonstration of its capabilities occurred in January 2026, when h2oGPTe processed hundreds of invoices using JSON schema extraction. The system achieved 100% accuracy in retrieving documents with specific expiration dates (e.g., 03/31/2026) from a set of 10 agent-generated PDFs. Michelle Tanco, Head of Product at H2O.ai, explained the broader vision:
"The future of document intelligence isn't just semantic search, it's the intelligent fusion of structured and unstructured data retrieval".
This smooth integration ensures that repositories can keep pace with the evolving standards of digital libraries.
3. MindsDB
MindsDB operates as a federated query engine, allowing seamless connections to data sources without the need for data relocation or transformation. Sidney Rabsatt, Chief Product Officer at MindsDB, highlighted this benefit:
"The Federated Query Engine seamlessly connects to data sources without requiring complex data movement or transformation, preserving data privacy and security."
With more than 500,000 deployments and over 38,000 GitHub stars as of early 2026, MindsDB has demonstrated its effectiveness across a variety of use cases. These features form the backbone of its advanced document processing capabilities.
PDF Handling
MindsDB uses its Knowledge Bases feature to index unstructured documents through vector search and embedding models. A standout tool, aipdf, leverages generative AI models like GPT and Ollama to perform OCR on PDFs. This transforms scattered documents, such as research papers, into a searchable semantic layer that users can explore using natural language queries [30,32].
Automation Features
Building on its document indexing capabilities, MindsDB automates essential data synchronization processes. Its JOBS feature simplifies real-time data synchronization and transformation tasks, enabling faster processing of repository data. The platform also uses automated agent orchestration, allowing AI agents to interpret natural language queries and seamlessly coordinate between SQL and semantic operations. According to MindsDB's documentation, these tools can cut insight extraction time from five days to under five minutes.
Scalability
MindsDB is designed to handle real-time processing across large-scale data environments. Built for enterprise-level, petabyte-scale data, the platform includes over 200 pre-built connectors for databases, vector stores, and file systems. These integrations enable MindsDB to function as an Enterprise Data Gateway without requiring data to be moved [29,31]. Haim Cohen, a Software Engineer, commented on the platform’s scalability:
"MindsDB handles scaling in a way that is not visible to users, simplifying the complexity but leaving users with some basic questions about the scaling process."
Repository Compatibility
MindsDB integrates with repository systems through specialized handlers, such as a GitHub handler that lets users query repository issues and pull requests using SQL-like commands. Establishing these connections is straightforward; users can execute a CREATE DATABASE command with an API key or repository URL. For production environments, MindsDB advises setting up an ML task queue using Redis to prevent memory errors during resource-heavy operations like model training. This seamless setup ensures open-access repositories remain efficient and secure, even in AI-driven research workflows.
sbb-itb-f7d34da
4. OpenCV
OpenCV steps into the world of visual data, offering a practical solution for handling challenges in open access repositories. This lightweight, open-source computer vision library is designed to automate tasks with minimal computational needs. Its ability to operate efficiently on standard hardware makes it an appealing choice for institutions with limited budgets or infrastructure.
PDF Handling
When it comes to document layout analysis, OpenCV stands out with its heuristic-based pipelines. A noteworthy example is SPARTAN (Structured Parsing and Relevant Table Analysis), introduced in July 2025. This open-source pipeline leverages OpenCV modules to automate table detection in documents. Tested on over 20,000 pages, SPARTAN demonstrated impressive results: 0.94 precision, 0.91 recall, and an average processing time of 4.2 seconds per page, all while using just 1.2 GB of RAM. Its OCR accuracy hit 96.7%, making it a reliable tool for large-scale tasks.
Automation Features
OpenCV simplifies the extraction of complex tabular data from scientific papers and reports without relying on GPUs or deep learning models. Research Square highlights its practicality:
"SPARTAN's CLI-governed, swap-in-swap-out architecture encourages domain tuning, edge deployment and cloud-scalable REST service wrapping, making it a practical bridge between brittle rule systems and heavyweight AI."
In 2020, the University of Calgary's Libraries and Cultural Resources explored OpenCV's potential in a case study. They used locally hosted AI tools, including OpenCV-based environments, to automate metadata creation for 114 archival images. Digital Metadata Librarian Ingrid Reiche and Technology Support Analyst Karynn Martin-Li led the project, which employed pre-trained models to generate captions and titles. The MS COCO model provided usable descriptive metadata for 53% of the images, offering a feasible local solution for processing sensitive archival data. This level of automation aligns with the repository workflow improvements discussed earlier.
Scalability
OpenCV's design makes it a strong candidate for large-scale repository tasks. Its support for hardware acceleration through cv::UMat minimizes CPU–GPU transfer overhead by keeping data in GPU memory during processing. Additionally, OpenCV's optimized intrinsics take advantage of modern server architectures like AVX-512, ARM SVE2, and RISC-V RVV. Unlike deep learning pipelines that demand significant GPU resources, OpenCV-based heuristics handle complex PDF processing with a minimal memory footprint, ensuring efficiency.
Repository Compatibility
As an open-source tool that can be hosted locally, OpenCV offers repositories a way to automate metadata creation - generating descriptions, titles, and keywords - while keeping full control over their data. This is particularly important for adhering to restrictive donor agreements and maintaining data sovereignty. By handling metadata automation in-house, OpenCV eliminates the need for costly per-page fees (which can range from $0.60–$1.50 per 1,000 images) and avoids the risks associated with cloud-based processing.
5. Keras
Keras brings deep learning capabilities to open-access platforms, making it easier for repositories to leverage advanced technology. This high-level API supports multiple backends - JAX, TensorFlow, and PyTorch - allowing repositories to choose the best option for their hardware. As an open-source tool under the Apache 2.0 license, Keras fits naturally into academic and research settings.
Automation Features
Keras simplifies complex processes with its pretrained "task" models available through KerasHub and Keras Applications. These tools provide ready-to-use models like BERT, GPT2, and YOLOv8, complete with built-in preprocessing, reducing setup time. For those less experienced in deep learning, AutoKeras automatically tunes architectures and hyperparameters, streamlining workflows. With nearly 3 million developers using Keras as of early 2026, its popularity speaks volumes about its ease of use and functionality.
Scalability
Designed for large-scale operations, Keras uses XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) compilation to boost performance by speeding up execution and cutting down memory usage. The tf.data API processes data through a compiled graph, preventing bottlenecks during data ingestion, even with massive datasets. Depending on the backend, benchmarks show performance improvements ranging from 20% to 350%. Additionally, the Distribution API, particularly effective with JAX backends, supports parallel processing for both data and models in high-performance computing environments.
Repository Compatibility
Keras integrates seamlessly into existing Python-based repository systems, making it an excellent choice for academic and research repositories. Domain-specific packages like KerasCV and KerasNLP enable tasks such as computer vision and natural language processing, which are essential for extracting structured data from scientific PDFs. Its modular design allows for custom preprocessing pipelines tailored to a repository's needs. Plus, its backend-agnostic nature ensures that automation scripts remain functional across JAX, TensorFlow, or PyTorch without requiring code modifications.
Advantages and Disadvantages
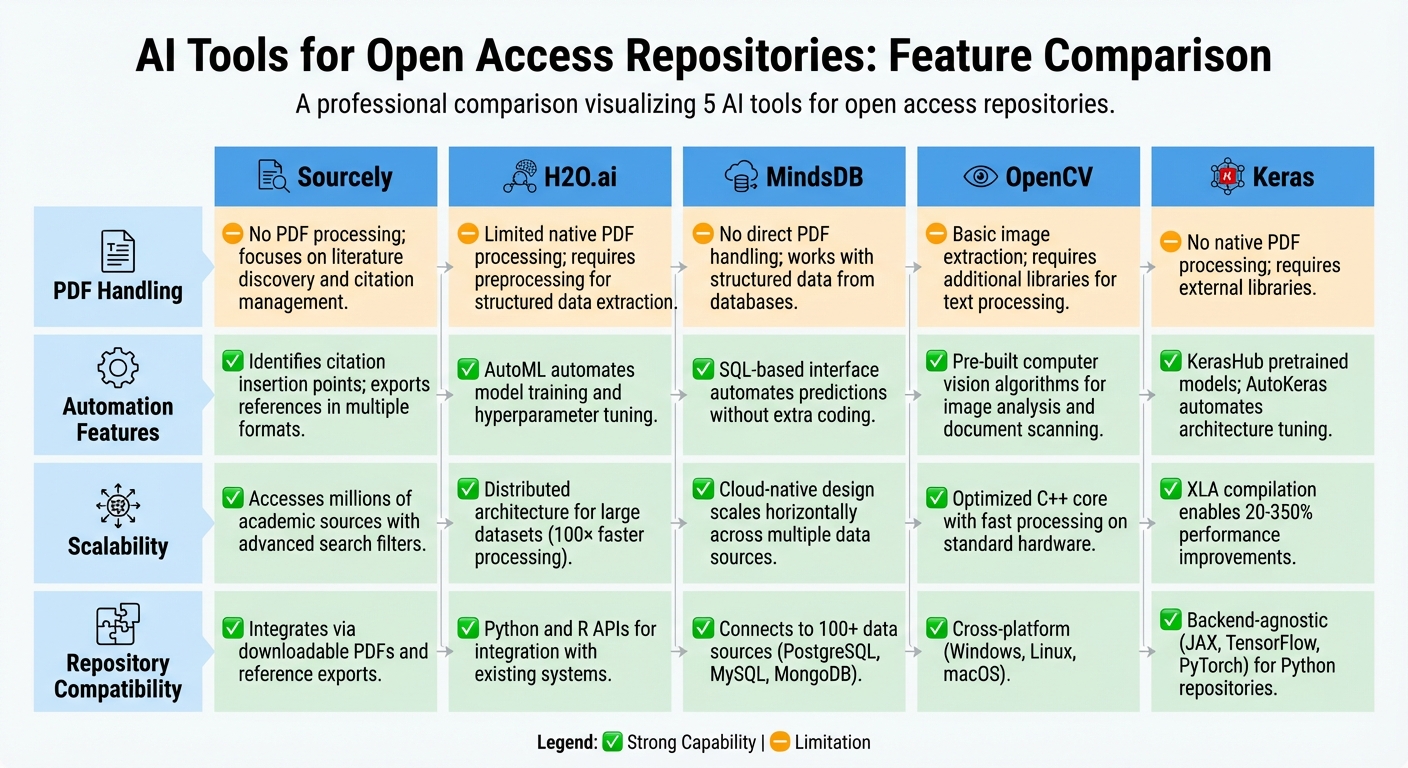
Comparison of 5 AI Tools for Open Access Repositories: Features and Capabilities
This section offers a clear comparison of the tools discussed earlier, focusing on how they perform in key areas like PDF handling, automation, scalability, and compatibility with repositories. The table below provides a side-by-side view of these metrics, making it easier to understand each tool's strengths and limitations.
| Tool | PDF Handling | Automation Features | Scalability | Repository Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sourcely | Does not process PDFs; focuses on literature discovery and citation management | Identifies insertion points for sources and exports references in multiple formats | Accesses millions of academic sources with advanced search filters | Integrates with academic workflows via downloadable PDFs and reference exports |
| H2O.ai | Limited native PDF processing; requires preprocessing for structured data extraction | AutoML capabilities automate model training and hyperparameter tuning | Distributed architecture efficiently handles large datasets | Python and R APIs enable integration with existing repository systems |
| MindsDB | No direct PDF handling; works with structured data from databases | SQL-based interface automates predictions and enriches data without extra coding | Cloud-native design scales horizontally across multiple data sources | Connects to 100+ data sources, including PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MongoDB |
| OpenCV | Basic image extraction from PDFs; requires additional libraries for text processing | Pre-built computer vision algorithms automate image analysis and document scanning | Optimized C++ core with Python bindings delivers fast processing on standard hardware | Cross-platform compatibility (Windows, Linux, macOS) fits diverse repository environments |
| Keras | No native PDF processing; requires external libraries for document handling | KerasHub offers pretrained models with built-in preprocessing; AutoKeras automates architecture tuning | XLA compilation and distribution APIs enable performance improvements depending on backend | Backend-agnostic design (supports JAX, TensorFlow, and PyTorch) ensures flexibility for Python-based repositories |
Key Trade-Offs
Each tool shines in its own niche, but their limitations are equally important to consider:
- Specialized vs. Generalized Capabilities: Sourcely is tailored for literature discovery and citation management, making it a go-to for academic workflows. However, it cannot process repository documents directly. On the other hand, tools like Keras and H2O.ai bring advanced machine learning and automation capabilities but demand technical expertise to set up custom PDF processing pipelines.
- Scalability: H2O.ai's distributed architecture is designed for massive datasets, which might be overkill for smaller repositories. MindsDB's cloud-native approach offers horizontal scaling but could introduce dependencies on external infrastructure. Meanwhile, Keras's performance varies depending on the backend used, making scalability somewhat situational.
- PDF Handling: OpenCV provides strong computer vision functionality, but additional tools are needed for comprehensive text extraction. Similarly, Keras and H2O.ai lack native PDF processing and rely on external libraries for document handling.
This comparison highlights the importance of aligning tool selection with your specific repository needs, whether you prioritize automation, scalability, or compatibility.
Conclusion
Sourcely is crafted to address a wide range of repository needs, offering both precision and efficiency. By connecting researchers to millions of academic sources and identifying exactly where citations are needed, it stands out as a powerful AI tool for academic literature discovery and citation management. Features like advanced search filters and automated reference exports streamline research workflows, making the process faster and more organized.
As Russell Michalak, Director of Library and Archives at Goldey-Beacom College, aptly put it:
"That shift - from authoring every word to reviewing and governing at scale - is the difference between backlog and discovery."
The use of a human-in-the-loop model, where AI handles the drafting and experts oversee the review process, ensures both quality and efficiency. This approach not only upholds high standards but also significantly improves the way research workflows are managed. Sourcely strikes this balance perfectly, allowing researchers to dedicate more time to analysis and discovery instead of being bogged down by manual literature searches.
FAQs
Which AI tool is best for my repository’s needs?
When choosing the best AI tool for your repository, it all comes down to your specific needs. Are you looking to automate tasks, integrate with existing systems, or decide between open-source and proprietary solutions? Tools like Elicit and Scholarcy are fantastic for research assistance and literature reviews. Meanwhile, other tools specialize in areas like metadata management or streamlining workflows. If your requirements are unique, open-source or customizable options might be the way to go. The key is to pick a tool that matches your goals - whether that's literature discovery, managing metadata, or synthesizing information.
How can I automate metadata tagging without losing accuracy?
To streamline metadata tagging with precision, utilize AI tools tailored to detect and enhance metadata elements such as entities, dates, and crucial details. These tools, including specialized AI models or metadata assistants, help maintain proper syntax, consistency, and formatting. Incorporating a human-in-the-loop approach adds a layer of validation and correction, ensuring high-quality results. This blend of AI-driven processes and human review is particularly useful for handling intricate or high-stakes scenarios, delivering both efficiency and dependability in metadata automation.
What’s the safest way to use AI while protecting sensitive repository data?
To use AI responsibly while protecting sensitive repository data, it's crucial to strike a balance between accessibility and security. Start by controlling machine access to your data. This can be achieved with tools like robots.txt files, CAPTCHAs, or IP filtering to prevent unauthorized scraping.
Legal protections are another essential layer - consider implementing licensing agreements that clearly define how your data can be used. Additionally, following community-driven guidelines helps promote ethical AI practices. These steps not only safeguard your repository's integrity but also support open access principles in a responsible way.