
Manual Searching vs. AI Discovery: Which Finds Better Sources?
When it comes to finding academic sources, manual searching and AI discovery tools each offer distinct advantages and drawbacks. Here's the bottom line:
-
Manual Searching:
- Best for thoroughness and accuracy.
- Captures nearly all relevant studies (94.5% sensitivity).
- Time-intensive, often requiring weeks or months.
- Low precision (7.55%), meaning many irrelevant results need sorting.
- Ideal for systematic reviews and in-depth research.
-
AI Discovery Tools:
- Prioritize speed, processing thousands of articles in minutes.
- Higher precision (41.8%), reducing irrelevant results.
- Lower sensitivity (39.5%), missing some key studies.
- May generate errors or fabricated references, requiring verification.
- Useful for quick searches, preliminary research, or high-volume tasks.
Quick Takeaway: Manual methods are more reliable but slow, while AI tools are faster but less thorough. A hybrid approach - starting with AI for speed and refining with manual searches - balances efficiency with accuracy.
Quick Comparison
| Feature | Manual Searching | AI Discovery Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Weeks to months | Minutes |
| Sensitivity | 94.5% | 39.5% |
| Precision | 7.55% | 41.8% |
| Best For | Systematic reviews | Preliminary searches |
| Drawbacks | Time-intensive | Risk of errors, low sensitivity |
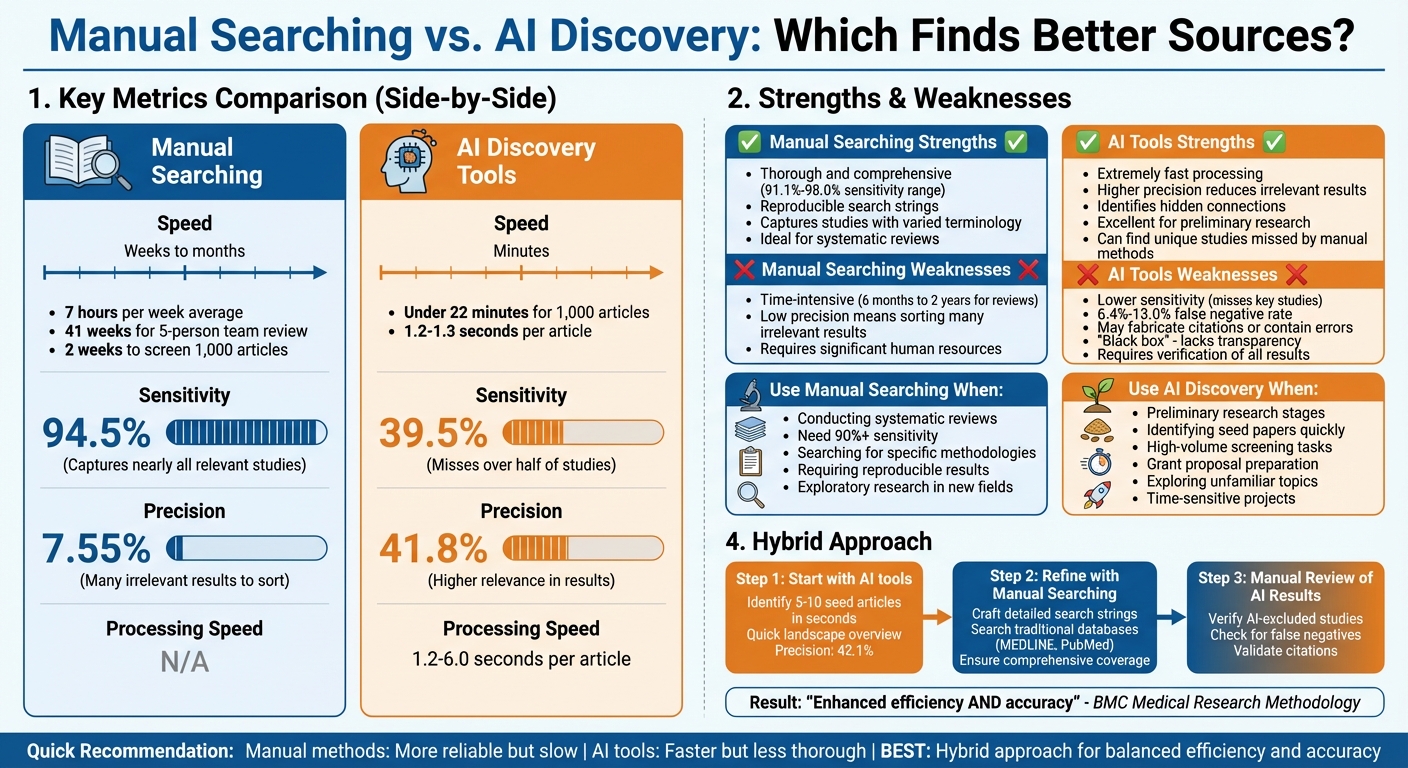
Manual vs AI Academic Source Discovery: Speed, Accuracy and Best Use Cases Comparison
Speed and Efficiency: Time Required to Find Sources
Manual Searching Takes More Time
Searching for sources manually can be a time-consuming process. On average, scientists dedicate about 7 hours per week to literature searches. When you factor in tasks like crafting keyword strategies, searching across multiple databases, screening articles, performing full-text reviews, and mining references, a five-person team may spend 41 weeks completing a single literature review.
For instance, manually screening a dataset of 1,000 articles typically takes around two weeks. Many systematic reviews also require a double-screening process, where two researchers independently review the same materials to eliminate bias. While this diligence ensures higher-quality research, it also significantly extends project timelines. However, AI-powered tools offer a way to cut down on this extensive time commitment.
AI Tools Speed Up Source Discovery
AI tools revolutionize the process by automating some of the most time-intensive tasks. Take Sourcely, for example - it can process a dataset of 1,000 articles in just under 22 minutes. These tools evaluate individual articles at lightning speed, taking only 1.2 to 1.3 seconds per article, compared to the weeks or months required for manual methods.
Beyond speed, AI tools handle tasks like developing search strategies, instantly generating inclusion and exclusion criteria, and mapping citations. For researchers tackling preliminary searches or working on grant proposals, this means they can move from a research question to relevant sources in mere minutes instead of days.
AI Tools for Literature Searching (June 2024)
Accuracy and Relevance: Comparing Result Quality
While speed matters, the quality of sources ultimately defines the success of your research. The question isn't just how fast you can find studies, but whether your method uncovers accurate, relevant ones - and avoids missing critical data.
Manual Searching: Leveraging Expertise for Accuracy
Manual searching shines when it comes to thoroughness. Researchers using traditional methods achieve an impressive sensitivity rate of 94.5% on average, meaning they capture nearly all relevant studies. However, this thoroughness comes at a cost: low precision. With an average precision of just 7.55%, researchers often end up sorting through a mountain of irrelevant articles to find the gems.
This high recall stems from the nuanced judgment of researchers, who can recognize relevant studies even when terminology varies. For example, in September 2025, Oscar Lau and Su Golder from Hull York Medical School compared manual searches to AI tools across four case studies, covering topics like vaping harms and breast reconstruction. Their manual searches achieved sensitivity rates ranging from 91.1% to 98.0%, but this level of completeness required sifting through thousands of results.
"At the time of the evaluation, one AI tool did not achieve sufficient sensitivity to replace traditional literature searching, though its high precision may aid preliminary searches." - Su Golder, Department of Health Sciences, University of York
While manual searches excel at capturing nearly all relevant studies, their low precision makes them labor-intensive. This is where AI discovery tools take a different approach.
AI Discovery: Prioritizing Precision Through Algorithms
AI tools flip the script by focusing on higher precision. On average, AI tools achieve a precision rate of 41.8%, meaning a larger share of the results they provide are actually relevant. Platforms like Sourcely use algorithms to rank sources by relevance, placing the most useful articles at the top. This greatly reduces the number of irrelevant studies researchers need to review, especially during the early stages of research.
However, AI tools struggle with sensitivity. In the same September 2025 study, an evaluated AI tool averaged just 39.5% sensitivity, missing more than half of the studies identified through manual searches. For instance, in a January 2025 test on trapeziometacarpal osteoarthritis, manual searches uncovered 23 studies, while AI tools identified far fewer. One tool even had a 94% false positive rate, producing a flood of irrelevant results.
AI tools also face challenges with transparency. Unlike manual searches, which rely on reproducible search strings that others can verify, AI systems often operate as a "black box." This lack of transparency can complicate validation. Additionally, conversational AI models can introduce errors, such as fabricating citations, misquoting authors, or providing incorrect publication dates. As a result, every AI-generated result must be carefully verified before it can be trusted.
sbb-itb-f7d34da
When to Use Each Method: Practical Scenarios
Each research method has its strengths, and the choice depends on your specific needs. Here's how to decide which approach works best in different scenarios.
When Manual Searching Works Best
Manual searching is indispensable for systematic reviews and evidence syntheses, especially when precision is critical. If your research demands a high sensitivity rate - typically 90% or higher - to ensure no relevant studies are missed, traditional methods remain the gold standard. Manual searches are particularly adept at capturing nearly all relevant studies.
Traditional search engines like Google Scholar shine when you're looking for specific methodologies, exact phrases, or niche datasets buried within full-text articles. For instance, Google Scholar’s full-article indexing can help you track down technical details like software versions or experimental protocols. Additionally, manual searches often excel at uncovering foundational studies and highly cited "pillar" papers, thanks to citation-based algorithms.
This approach is also ideal for exploratory research, where running consistent queries is essential to map out a new field. The deterministic nature of manual searches - yielding the same results each time - ensures reproducibility, which is a cornerstone of academic research.
When AI Discovery Tools Work Best
AI discovery tools, on the other hand, are best suited for situations where speed and volume are critical.
These tools are incredibly useful in the early stages of research, helping you quickly identify key seed papers to refine your search strings for more detailed manual searches. For example, a recent umbrella review on the harms of vaping in young people found that an AI discovery tool identified two unique studies missed by manual methods, with a precision rate of 42.1% compared to 14.7% for manual searches.
AI tools are transformative for high-volume screening tasks. While manually reviewing titles and abstracts can take weeks, AI can process articles in just 1.2 to 6.0 seconds each. This makes AI invaluable for research topics overflowing with information, where manually filtering through thousands of results would be overwhelming. Platforms like Sourcely allow users to paste their essay and apply precise filters to locate relevant sources quickly.
Beyond speed, AI discovery tools can uncover hidden connections between different research areas, sparking new hypotheses and linking ideas that might be missed in traditional keyword-based searches. They also provide quick insights into unfamiliar topics and can assist with practical tasks like troubleshooting experimental procedures, calculating dilutions, or generating code for data visualization.
Using Both Methods Together: A Hybrid Approach
The best strategy combines the strengths of manual searches with the capabilities of AI tools. Between August and November 2024, Canada's Drug Agency Research Information Services experimented with this hybrid approach across seven agency projects. Their findings? AI tools are most effective when used as a complement to manual methods.
Here’s how this hybrid method plays out: Start with an AI tool like Sourcely to quickly pinpoint 5–10 high-quality "seed" articles. These articles provide a snapshot of the research landscape in just seconds. From there, craft detailed search strings manually and dive into traditional databases like MEDLINE or PubMed. This blend capitalizes on AI’s speed and precision while maintaining the depth and reliability of manual searches. The result is a process that balances rapid discovery with thorough exploration.
Research backs up this approach:
"A hybrid approach that integrates human expertise with AI may enhance both the efficiency and accuracy of the literature screening process." - BMC Medical Research Methodology
Human involvement is still crucial. While AI can screen articles in under 3 seconds - a task that would take weeks manually - it comes with a higher false negative rate, ranging from 6.4% to 13.0%. This makes manual review of AI-excluded studies essential to ensure no key research slips through the cracks. The hybrid method effectively combines AI’s speed with the meticulousness of human oversight.
For example, in an umbrella review on the harms of vaping among youth, researchers discovered two unique studies using AI that manual searches had missed due to gaps in database indexing. This highlights how blending both methods can deliver more comprehensive results efficiently.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Research
There’s no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to selecting a research method - it all depends on your goals. Manual searching, while thorough, is a time-consuming process that can take anywhere from six months to two years to complete a high-quality review. On the other hand, AI tools like Sourcely offer a different set of advantages. These tools shine in speed and precision, screening articles in seconds and delivering a much higher percentage of relevant results (41.8% precision compared to just 7.55% for manual methods). However, they come with a trade-off: they tend to miss more studies, with sensitivity around 39.5%. This makes AI particularly useful for tasks like preliminary research, identifying foundational papers, or preparing grant proposals - situations where speed is more critical than exhaustive coverage.
To get the best of both worlds, consider a hybrid approach. Start with AI tools to quickly identify key studies, then follow up with manual searching to ensure a comprehensive review. This combination allows you to leverage AI’s efficiency while still achieving the depth and rigor needed for thorough research.
Ultimately, the method you choose should align with the stakes and timeline of your research. AI methods can save time and provide rapid insights, while manual searching ensures a deeper dive into the literature. With scientists already dedicating an average of seven hours per week to literature searches, selecting the right approach for each task can help you make the most of that time.
FAQs
How can combining AI tools with manual research improve accuracy and efficiency?
A hybrid research approach blends the efficiency of AI-powered tools, like Sourcely, with the thoughtful analysis of human researchers. AI excels at quickly scanning massive datasets, identifying key ideas, and ranking sources by relevance - tasks that would otherwise take hours of manual effort. After AI creates an initial list of results, human researchers step in to refine the selection, verify accuracy, and tackle any subtleties that AI might overlook.
This partnership strikes a balance: AI handles repetitive tasks like keyword searches and removing duplicates, while human input ensures the results are accurate and contextually appropriate. Studies suggest this approach can cut research time by up to 50%, all while maintaining - or even improving - the quality of results. It’s a powerful method for academic projects that require both speed and precision.
What are the risks of depending only on AI tools for finding research sources?
Relying entirely on AI tools for research comes with its own set of challenges. For starters, AI algorithms can carry hidden biases, often favoring well-cited journals or trendy topics while overlooking lesser-known but equally important studies. Because many AI systems operate without full transparency, it’s tough to determine how results are ranked - or if critical studies are being left out.
Another issue is the risk of inaccurate or even fabricated references. As AI-generated content becomes more prevalent, the chance of encountering unreliable citations increases, potentially undermining the credibility of your research. AI tools also struggle with subtleties like identifying methodological flaws or understanding complex, domain-specific details - areas where human expertise shines.
Lastly, leaning too heavily on AI can erode your own research skills. Over time, this reliance might make it harder to validate findings or perform manual searches when necessary. To maintain high-quality research, it’s essential to strike a balance: use AI as a helpful tool, but combine it with manual verification and a critical eye.
When is manual searching better than using AI tools for finding academic sources?
Manual searching proves especially useful when tracking down studies that AI tools might overlook. This can include older publications, materials in languages other than English, or "grey literature" such as conference proceedings and niche journal articles that aren't fully indexed in major databases. Researchers aiming for thorough coverage often rely on manual techniques to make sure they don’t miss any critical studies.
Another strength of manual searching lies in its ability to incorporate expert judgment when evaluating the relevance or quality of sources. While AI tools can pull up a vast number of papers, they often fall short when it comes to meeting nuanced inclusion criteria or understanding subtle methodological details. For instance, human researchers can pick up on key insights in highly specialized areas that automated systems might fail to detect. When precision and depth are top priorities, manual searching remains a dependable method.